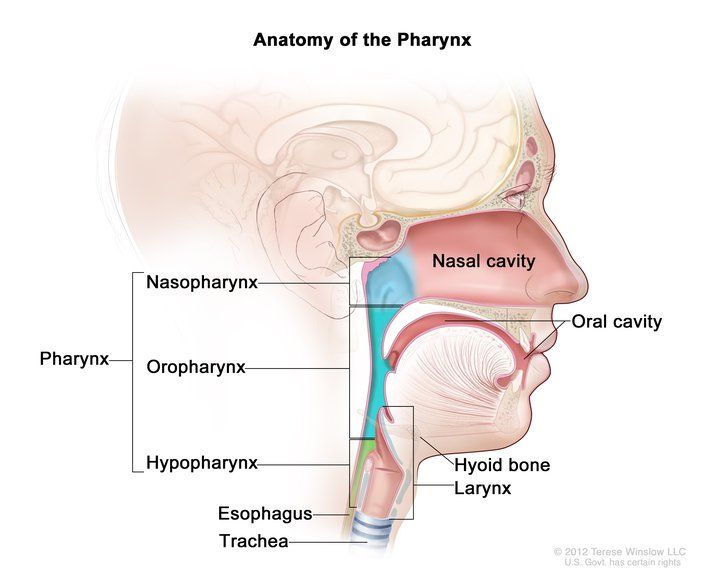
The pharynx is a hollow tube about five inches long that starts behind the nose and leads to the esophagus (food pipe) and the larynx (voice box).
The pharynx has three parts:
- Nasopharynx: The upper part of the pharynx is called the nasopharynx. It’s the area of your throat right behind your nose.
- Oropharynx: The oropharynx is the middle part of the pharynx. It includes the soft palate, the soft area right behind the hard roof of your mouth; the back one-third of your tongue (base of the tongue); and your tonsils.
- Hypopharynx: The hypopharynx is the lower part of the pharynx that funnels food to the esophagus (food pipe).
What causes throat cancer?
Infection with the sexually transmitted human papillomavirus (HPV) — a virus that infects the skin and can cause abnormal tissue growth — has been linked to 70% of cancers of the mouth and throat (oropharyngeal cancers). Smoking and heavy drinking are also major risk factors for this disease.
Over the past several years, the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted disease, has been linked to a growing number of throat cancers. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that in the U.S., 70% of oropharyngeal cancers are caused by HPV. (It could be that these cancers are not caused by HPV alone but develop when someone who has HPV also uses tobacco and/or drinks alcohol.)
What are the symptoms of throat cancer?
- A lump or mass in the neck
- Difficulty swallowing, or pain when swallowing
- Hoarseness or change in voice
- Sore throat that doesn’t go away
- Ear pain or ringing in the ears
- Hearing loss in one ear
- Bad breath that doesn’t go away
- Breathing difficulty
- Difficulty speaking
- Blood-tinged saliva
- Double vision
- Frequent headaches