A hallmark feature of PDAC is an extensive desmoplastic stroma comprised of myofibroblasts (MF), extracellular matrix (ECM), and immune cells.
Most studies have focused on cytotoxic T cells, NK cells and M1 macrophages in inhibiting tumor initiation and progression. Less explored is the potential role of the immune cells, which are early responders to the mutation events in PDAC, especially CD4+ cells in disease promotion.
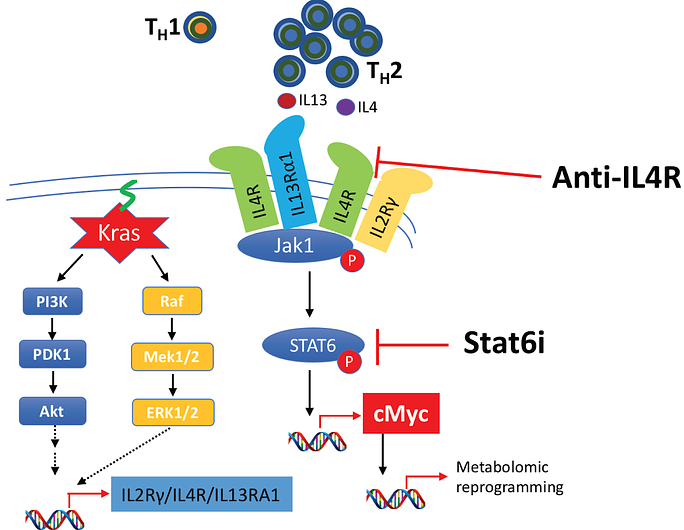
CD4+ T helper cells, with their multiple subtypes (TH 1, 2, 9, 10, 17, 22) are critical for inflammatory processes in cancer. Among them, TH2 subtypes can promote tumor growth via various mechanisms that include induction of M2 macrophage polarization.
Previously, we have identified a unique role of TH2 polarized CD4 T-cells in collaborating with oncogenic Kras in transforming indolent PanIN into malignant pancreatic tumor. Our data show an important role of tumor infiltrating TH2 cells and its prototypic cytokines IL4 and IL13 driving tumor initiation and progression.
Concurrently, oncogenic Kras upregulates the expression of cytokine receptors IL2rg, IL4ra and IL13ra1 that, upon IL4 and IL13 engagement, activates the Jak1-Stat6 pathway.
The goal of this project is to identify factors that are released by cancer cells that attract TH2 cells into the tumor microenvironment and if blocking of TH2 infiltration mediated pathway has any therapeutic benefit.
Contact the Dey Lab
Email: Prasenjit.Dey@RoswellPark.org
Phone: 716-845-1300, x5269
Office location: Center for Genetics & Pharmacology (CGP) L5-307
Lab Location: Center for Genetics & Pharmacology (CGP) L15-115
Department of Immunology
Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center
Elm and Carlton Streets
Buffalo, NY 14263