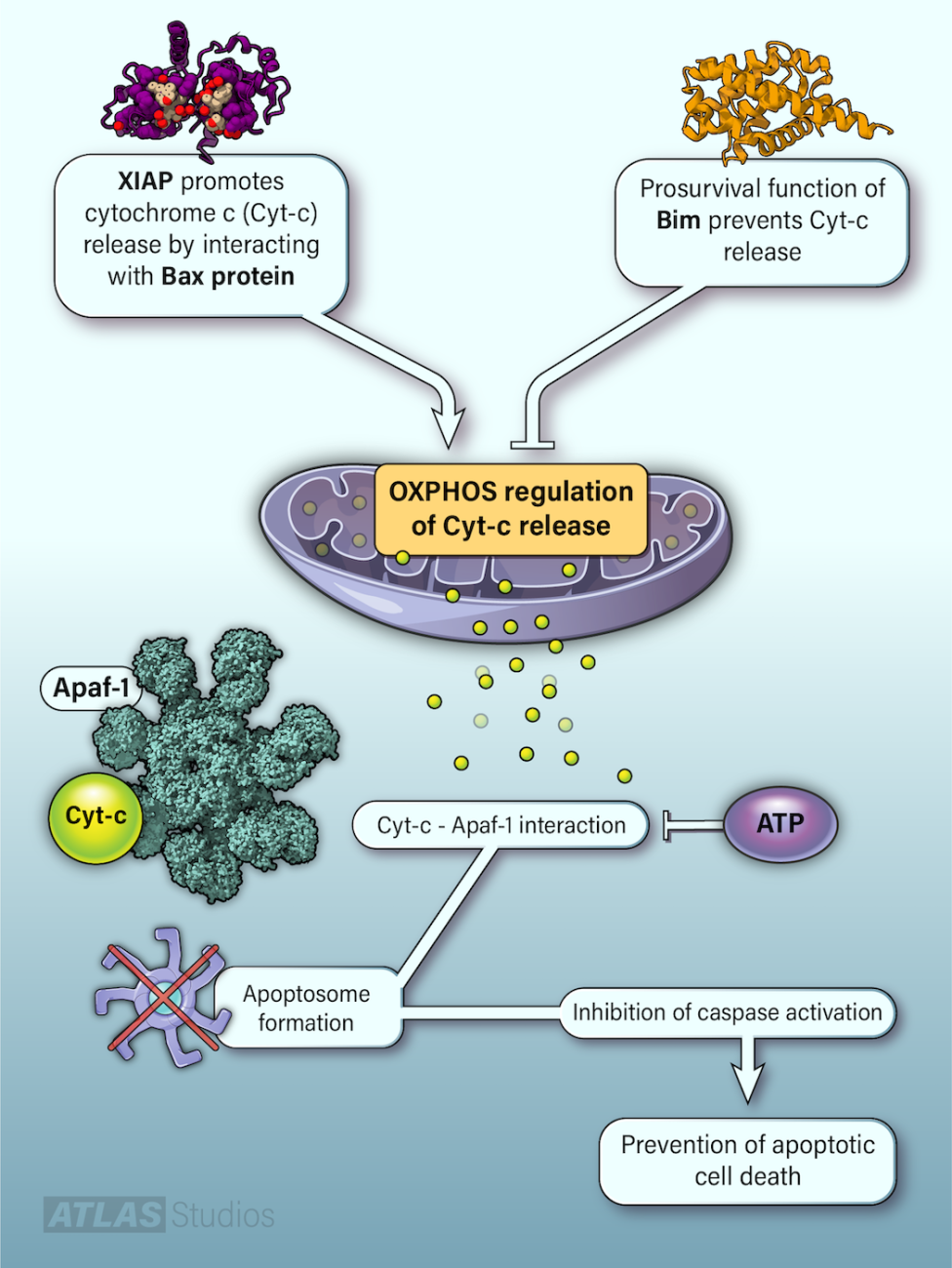
Release of mitochondrial cytochrome c initiates the apoptosome (a multimeric protein complex) formation leading to caspase activation and apoptosis. We have discovered various mechanisms that regulate apoptosome formation and function in cancer cells.
Nucleotide regulation of apoptosome formation and function
We have identified that physiological levels of nucleotides bind cytochrome c, and therefore block the most upstream events in the apoptosome formation (i.e., cytochrome c-Apaf-1 interaction), which inhibits caspase activation and apoptosis.
We have dissected the important role for lysine residues of cytochrome c and nucleotides in the regulation of apoptosome-dependent apoptotic cell death as well as demonstrate how these mutations and nucleotides may have a pivotal role in understanding human diseases such as cancer.
Novel regulation of apoptosome by XIAP, Bim, and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS)
Bim, a proapoptotic BH3-only protein, plays a critical role in Bax/Bak channel formation causing mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. We observed that Bim is highly upregulated in cancer cells and harbors a novel prosurvival function in cancer.
We identified a novel proapoptotic function of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), which is considered as a prosurvival protein. We observed that global dynamic structural changes of key macromolecules (including proteins, lipids, DNA, and RNAs) during apoptosis at mitochondria represents a new hallmark of apoptosis. We define that restoration of the OXPHOS system is essential for cell death induction.
New avenues to target mitochondria
These findings may lead to development of novel anticancer agents targeting novel function of Bim, XIAP, and OXPHOS in cancer. These findings provide avenues to target mitochondria either by single agent or in combination for overcoming resistance and prevention of recurrence of various types of cancer including prostate cancer.
Related publications
- Yadav N, et al. Molecular insights on cytochrome c and nucleotide regulation of apoptosome function and its implication in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020 Jan;1867(1):118573. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.118573. Epub 2019 Oct 31. PMID: 31678591; PMCID: PMC7733678.
- Yadav N, et al. Oxidative phosphorylation-dependent regulation of cancer cell apoptosis in response to anticancer agents. Cell Death Dis. 2015 Nov 5;6(11):e1969. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.305. PMID: 26539916; PMCID: PMC4670921.
- Yadav N, et al. Transformations of the macromolecular landscape at mitochondria during DNA-damage-induced apoptotic cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2014 Oct 9;5(10):e1453. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.405. PMID: 25299778; PMCID: PMC4649512.
- Gogada R, et al. Bim, a proapoptotic protein, up-regulated via transcription factor E2F1-dependent mechanism, functions as a prosurvival molecule in cancer. J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 4;288(1):368-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.386102. Epub 2012 Nov 14. PMID: 23152504; PMCID: PMC3537034.
- Gogada R, Prabhu V, Amadori M, Scott R, Hashmi S, Chandra D. Resveratrol induces p53-independent, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP)-mediated Bax protein oligomerization on mitochondria to initiate cytochrome c release and caspase activation. J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 19;286(33):28749-60. PMID: 21712378.
- Chandra D*, Bratton SB, Person MD, Tian Y, Martin AG, Ayres M, Fearnhead HO, Gandhi V, Tang DG*. Intracellular nucleotides act as critical prosurvival factors by binding to cytochrome C and inhibiting apoptosome. Cell. 2006 Jun 30;125(7):1333-46. PMID: 16814719. *Corresponding authors.
In the news
Connect with the Chandra Lab
Email: Dhyan.Chandra@RoswellPark.org
Phone: 716-845-4882
Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics
Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center
Elm and Carlton Streets
Buffalo, NY 14263