Roswell Park’s pathologists who specialize in bladder cancer will analyze your biopsy to learn valuable information about your cancer which helps to determine which treatments will be most effective. The pathology report includes critical information about your tumor, such as its:
- Cancer cell type
- Grade (low grade or malignant)
- Shape (flat or papillary)
- Invasive or noninvasive status
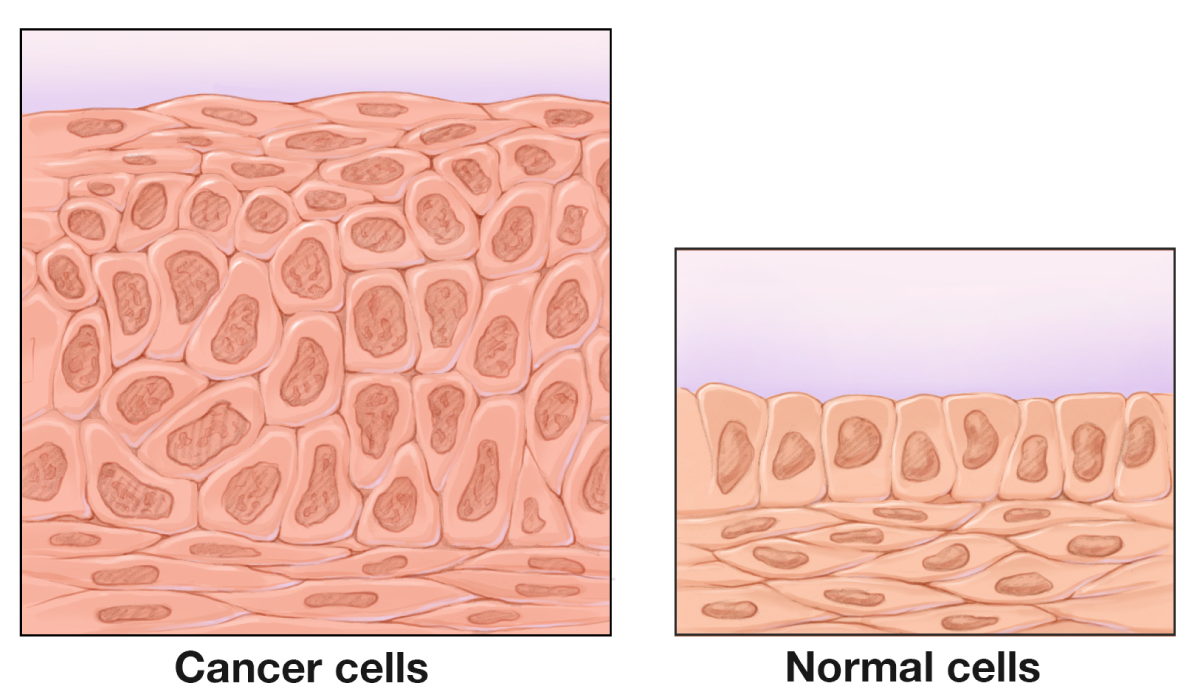
What is my bladder tumor’s cell type?
Your cancer’s cell type (also called histological type) refers to what the cell structure looks like under the microscope and how the cells are arranged. Bladder cancer includes many histological types:
- Transitional cell carcinoma is the most common bladder cancer type and accounts for about 90% of bladder cancers.
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma
- Small cell carcinoma (includes neuroendocrine, micropapillary and mixed-pattern subtypes)
- Sarcomatoid/plasmacytoid
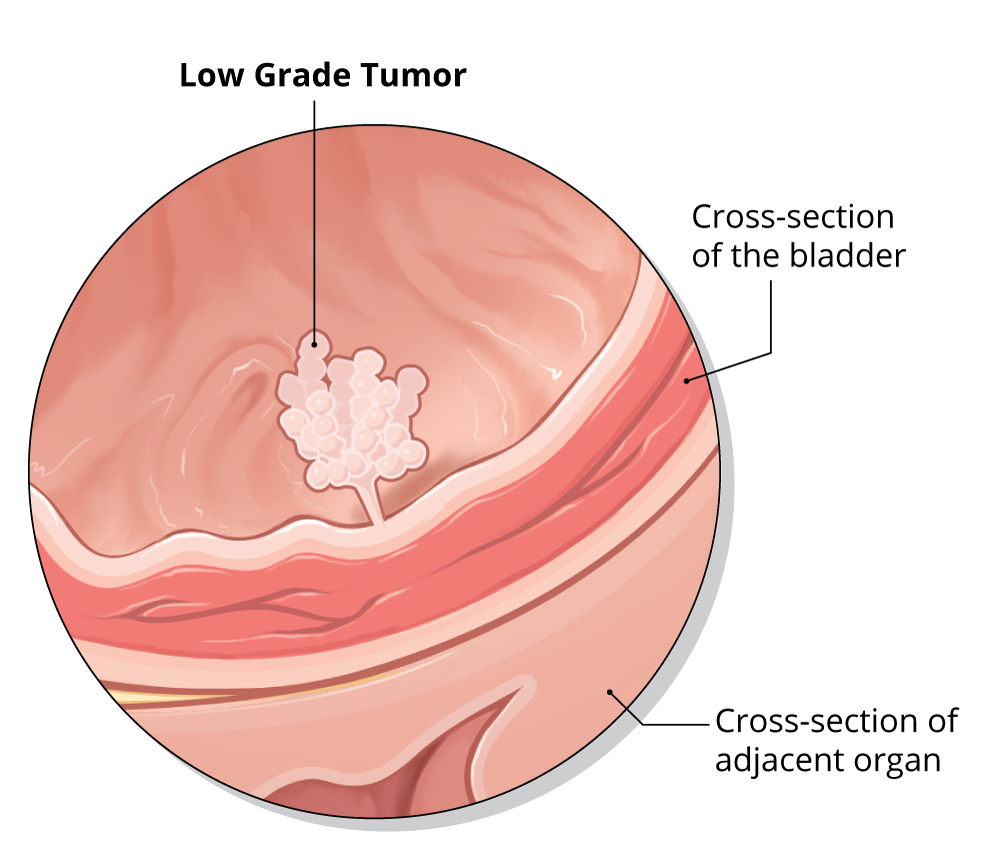
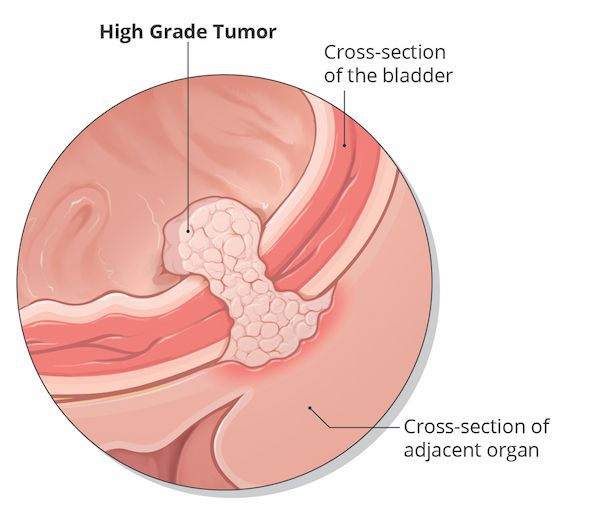
What is my bladder tumor’s grade?
Malignant tumors are classified as either low grade or high grade.
- Low-grade tumors grow slowly, and rarely invade other tissues or spread to other parts of the body.
- High-grade tumors are more likely to recur and may become invasive. These tumors contain cells that grow abnormally, and can invade other tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
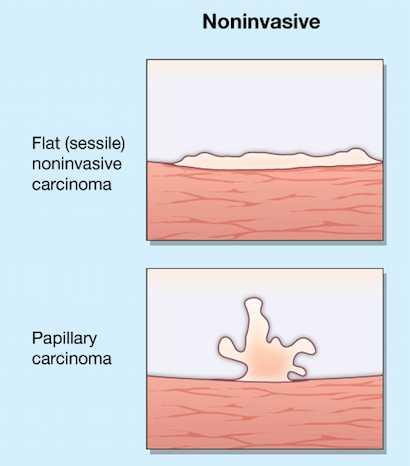
What is my bladder tumor’s shape?
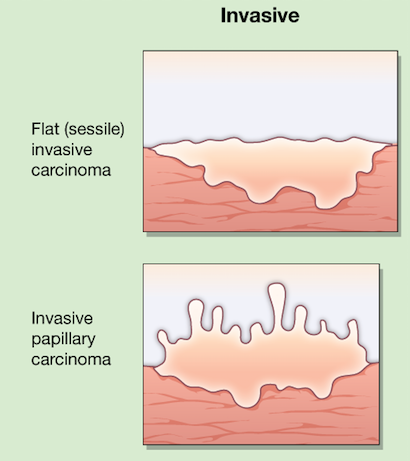
The shape of your tumor and whether or not it is invasive can tell your doctor how serious your bladder cancer is and the best way to remove it.
- Flat tumors (Sessile) are flat, superficial, spreading tumors. These tumors are often more difficult to treat.
- Papillary tumors have long, finger-like projections that stretch out from the bladder wall toward your bladder’s interior.
Is my tumor invasive or noninvasive?
These terms refer to whether or not your tumor has invaded or grown through the layers of the bladder wall.
- Invasive tumors grow into and/or through the bladder wall’s other layers.
- Noninvasive (in situ) tumors are contained in the bladder lining and do not grow through the other layers of your bladder.