Is there a screening test for kidney cancer?
Currently, there is not a recommended screening test for people who are at average risk for developing kidney cancer. People with certain genetic (inherited) conditions may be at increased risk for the disease, and may undergo regular imaging tests and/or urinalysis to detect kidney cancer early.
Am I at high risk for kidney cancer?
If you have two or more relatives with kidney cancer, you may be eligible for genetic testing to determine if you're at high risk for kidney cancer. If you test positive, you should undergo annual imaging of your kidneys to make sure they remain tumor-free.
Learn moreYou are considered at high risk for developing kidney cancer if you have:
- An inherited genetic condition such as von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome
- Multiple close relatives diagnosed with kidney cancer
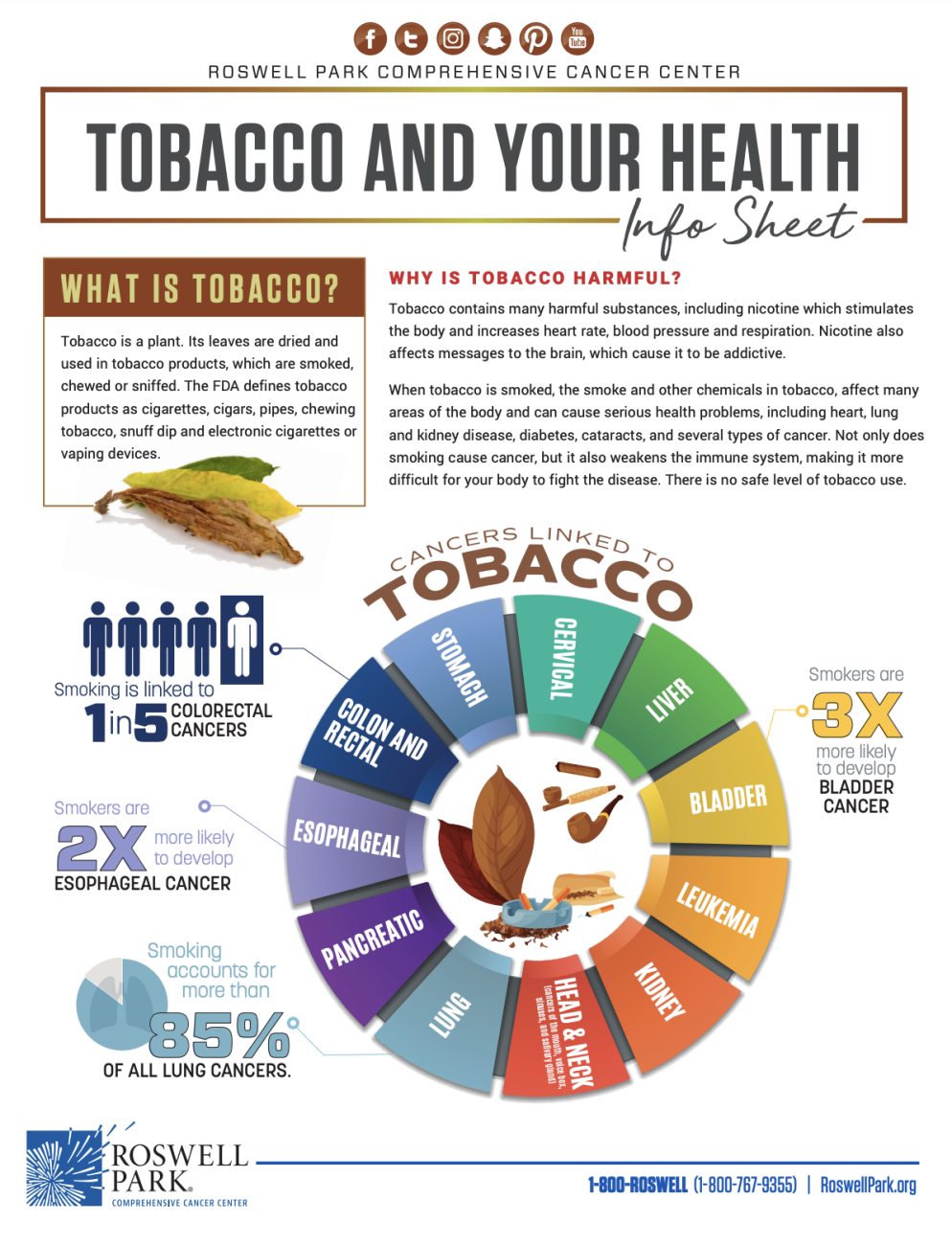
- A current or past history of smoking
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
If you are at high risk, talk to your physician about other measures that may be recommended for you such as careful observation and periodic urinalysis and imaging with CT or MRI scans.
What can I do to prevent kidney cancer?
Research has yet to pinpoint exactly what causes cells in the kidney to become cancerous, however you can take steps to reduce or eliminate some risk factors you may have and improve your chances for detecting it at its earliest, and most treatable stages. These include:
- Quit smoking. Smokers develop kidney cancer twice the rate of nonsmokers. You can do this, and we can help. Call the New York State Smokers’ Quitline at 1-866-NY-QUITS (1-866-697-8487) or visit www.nysmokefree.com for guidance, support and cessation aids. Roswell Park patients also have access to our Tobacco Cessation Treatment Program.
- Maintain a healthy body weight. People who are obese have an increased risk for many cancer types, including kidney cancer. Learn your body mass index (BMI) with a BMI calculator. A BMI of 25 to 29 indicates overweight; 30 or more is obese.
- See a physician regularly. Routine checkups with a primary physician can help detect and address risk factors such as high blood pressure, obesity and smoking. In addition, your physician may order an annual urinalysis, a urine test that can detect microscopic traces of blood in your urine — long before you would notice — that could indicate possible kidney cancer. (Blood in the urine has many causes, but you need an accurate diagnosis.)
Experts in urology care
If you are experiencing symptoms consistent with urinary issues, we urge you to complete our urologic cancer risk assessment form.