What we do
Drug Discovery Core Shared Resource (DDCSR) at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center provides investigators with the possibility of working on drug discovery and development within an academic institution. We provide guidance, expertise and technical support to investigators with all level of experience in drug development at all steps of the process, from target identification through assay development, small molecule screenings and hit validation.
We also provide our customers with access to more advanced stages of drug development such as structure activity relationship studies (SAR), hit to lead optimization (H2L) and analog testing in partnership with other expert resources. We work with our clients to make the development process a clear and efficient one.
Researchers at Roswell Park and outside biomedical institutions can get assistance with the design and execution of chemical screenings in a variety of readout systems and assistance with pre-screening and post-screening steps of drug discovery and development. Located on the Roswell Park campus, the Drug Discovery Core provides easy access to local investigators during all stages of discovery and development including:
- Target identification (assessment of target “drugability,” development of strategies to overcome undruggable targets, phenotype-based screening to find chemical probe for target discovery)
- Target validation (generation of tools to modulate target genetically, design and generation of genetic vectors: shRNA, CRISPR/Cas9, inducible, degradation based etc, generation of cells with modified expression/activity of target, running of assays to monitor target – phenotype effect)
- Assay design and optimization (assay selection: biochemical, cell based or in silico [partnership/collaboration], generation of cell lines, generation of cell-free biochemical assays, selection of appropriate controls)
- High throughput screening (providing access to variety of libraries and automation, work with custom libraries)
- Hit selection and confirmation Hit characterization
- Help with SAR studies and H2L via partnership with BioBlocks Inc, experts in medicinal and synthetic chemistry.
- Help with preclinical drug evaluation via partnership with other shared resources at Roswell ParkHelp with selection of a strategy of drug discovery and development, submission of grants, patent applications and understanding of the regulatory process
- Non-screening projects (genetic modification of cell lines, reporter cell line generation, cell characterization, storage and expansion, 2D and 3D cell culture, cell imaging, time lapse movies, cell migration, invasion experiments, fluorescent cell labeling, label-free cell counting etc)
- Experiment automation using our equipment (training required)
The collection of chemicals at the Drug Discovery Core totals more than 110,000 compounds. Sophisticated automated liquid handling equipment is used to ensure accurate delivery of this library in both the 96- and 384-well format, and our detection equipment allows for screening using either cell based or biochemical assays.
Compound libraries and equipment
Libraries
All libraries are available in both the 96- and 384-well format. Screening in the 384-well format is faster and less expensive, but some of the assays are incompatible with this high-density format. Below is the image delineating the location of compounds and empty wells used for controls on 96- and 384-well plates.
Equipment
Liquid handling group
Equipment used for automated delivery of liquid reagents and the transfer of compounds from the library to the assay plates in multi-well format.
- JANUS, PerkinElmer
- Compact Automated Reagent Dispensers
- D300e Digital Dispenser, Tecan
Detection group
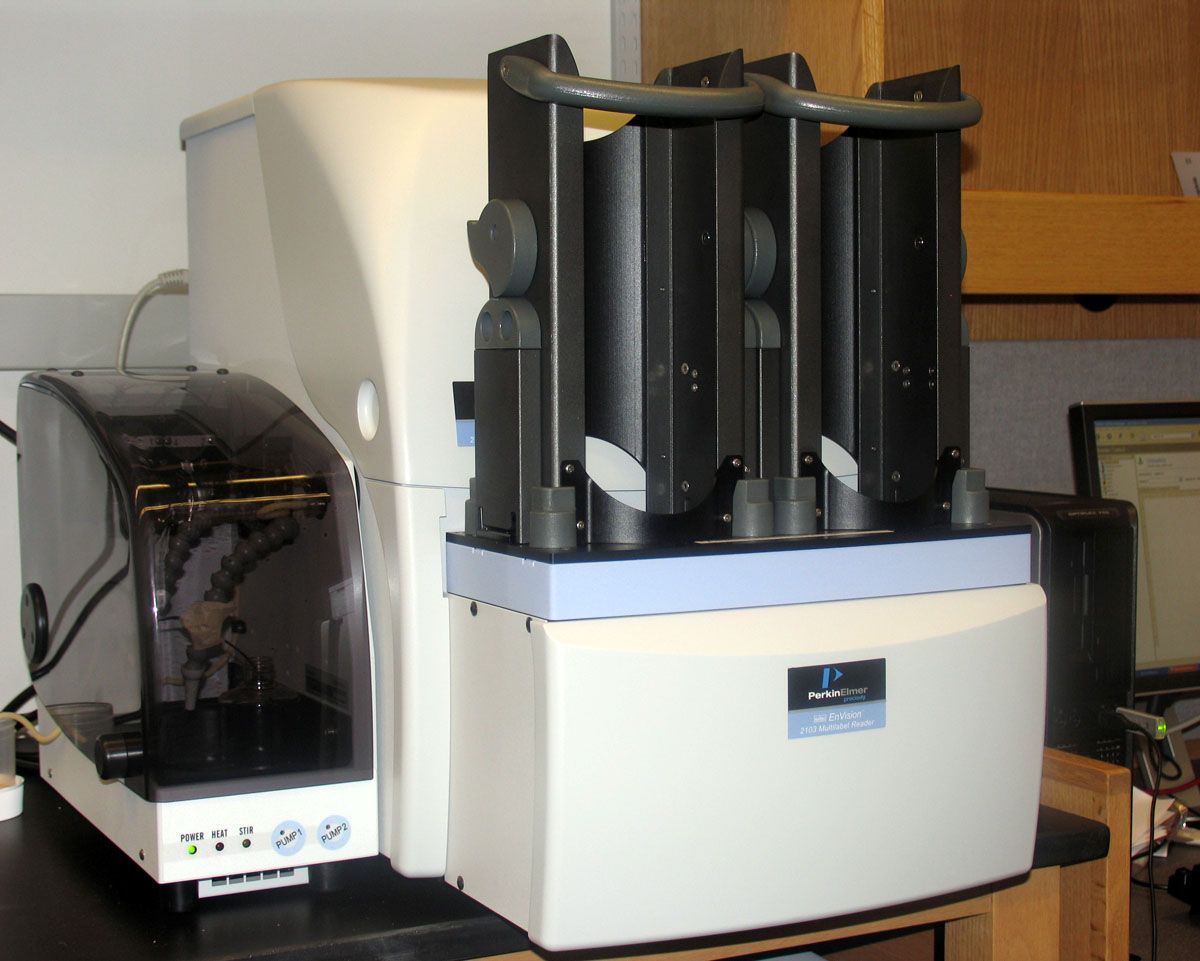
- EnVision Excite, PerkinElmer
- Cytation 5 with BioSpa 8, BioTek
TC complex
Dedicated tissue culture equipment simplifies the procedure of cell preparation for cell-based readout systems and the plating of cells in multi-well format.
Our tissue culture room is equipped with a laminar flow hood, CO2 incubators, water baths and automatic multichannel pipettors.
Historical libraries are collections of pre-existing organic compounds from different chemical labs selected based on their “drug-likeness,” and collections of pharmacological, bioactive or natural compounds. These libraries can be used for drug discovery as well as for “proof of principle” and assay validation experiments.
The Drug Discovery Core owns two historical libraries of diverse drug-like molecules for drug discovery projects:
- EXPRESS-Pick™ by ChemBridge Corporation (San Diego, CA): a diverse library of 55,230 compounds. This library consists of organic molecules with molecular weights in a range of 250 – 550, dissolved in DMSO at concentration 5mg/ml or 10-20 mM.
- HitDiscover by Maybridge (Part of Thermo Fisher): 52160 compounds dissolved in DMSO at 10mM concentration.
Historical libraries are collections of pre-existing organic compounds from different chemical labs selected based on their “drug-likeness,” and collections of pharmacological, bioactive or natural compounds. These libraries can be used for drug discovery as well as for “proof of principle” and assay validation experiments.
The Drug Discovery Core owns four historical libraries of known bioactive compounds:
- LOPAC1280 by Sigma (1280 compounds)
- Spectrum by MDS, Inc. (2000 compounds)
- Tocriscreen Total (1120 compounds)
- Tocriscreen Kinase Inhibitor Toolbox by Tocris Bioscience (80 kinase inhibitors)
- FDA-approved Drug Library by Selleckchem.com (1508 compounds)
These are libraries of pharmacological compounds dissolved in DMSO, to 10 mM or 1mM concentration (MW is < 500). These libraries include FDA and internationally approved drugs, and bioactive and natural compounds with described biological activity.
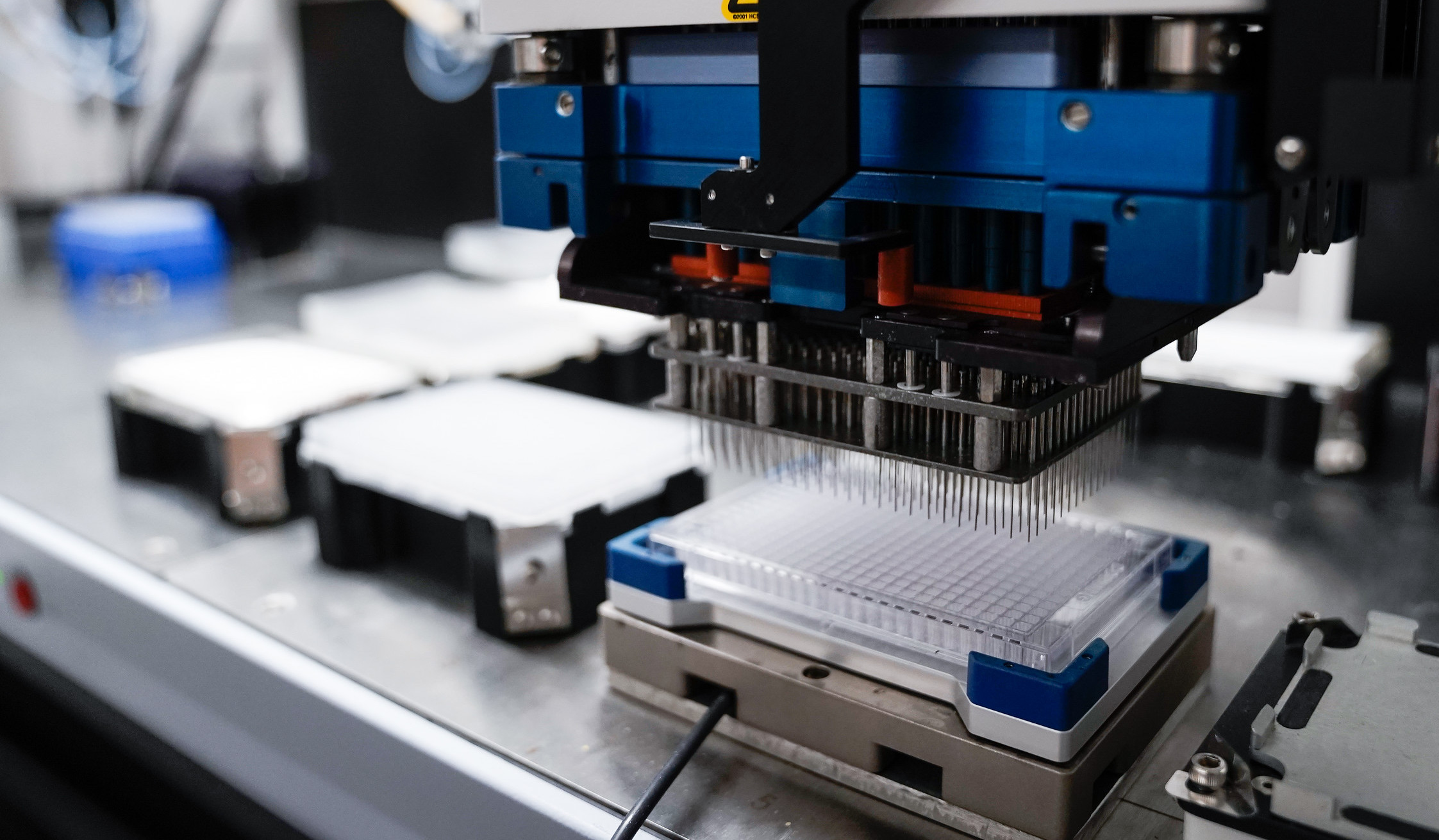
JANUS is capable of multichannel pipetting and reagent transfer in 96- and 384-well formats. Two heads (96- and 8-channel) provide great flexibility in choosing different pipetting modes:
- Simple reagent delivery to multiwell plates
- Automatic preparation of dilutions and different reaction Using two pin-tools, library compounds can be delivered to 96- and 384-well plates in nl volumes.
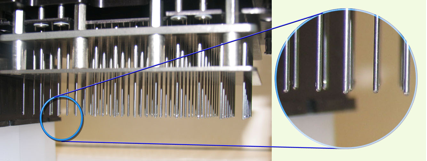
Using two pin-tools, library compounds can be delivered to 96- and 384-well plates in nl volumes (see figure).
96- and 384-pin tools designed for accurate transfer of compounds from the library to assay plate
Compact automated reagent dispensers, such as MicroFill and MicroFlo by BioTek, are designed to accurately and quickly distribute solutions to 96- and 384-well plates. The complete fluid pass of MicroFlo is autoclavable so that it can be used for automated plating of cells for cell-based assays.
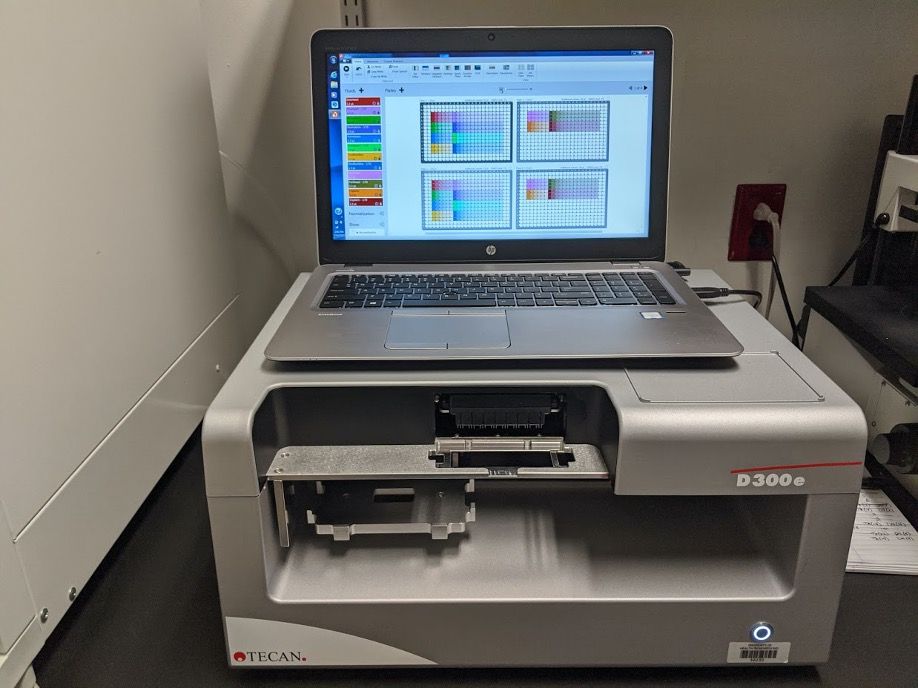
D300e Digital Dispenser
The D300e is a digital drug dispenser based on HP’s inkjet technology. The D300 allows the direct addition of liquids from compounds in DMSO to biomolecules in surfactant-containing aqueous solutions in picoliter-microliter range. It uses disposable dispensing chips in order to minimize dead volumes
of these liquids. The D300 is perfect for setting up your PCR and qPCR reactions, generating enzyme profiles, drug combinatorial experiments and dose-response curves.
This reader is the main workhorse in our facility. It can be used for a wide range of fluorescence, luminescence and photometry-based detection technologies, including the following list. It is also equipped with an excitation laser for AlphaScreen® applications.
- Fluorescence intensity
- Fluorescence polarization
- TRF (Time-resolved fluorescence)
- FRET (Fluorescence resonance energy transfer)
- Luminescence and enhanced luminescence
- Absorbance
- AlphaScreen®
EnVision requires a specific filter set for each detection technology. Currently, it is equipped with a set of filters for several routinely used assays.
If a new assay is required for screening, and the PI demonstrates a commitment and readiness to complete the screening, this reader can be easily upgraded with a new filter set.
EnVision can read in 96- and 384-well formats and is equipped with a plate stacker.
Cytation™ 5 Cell Imaging Multi-Mode Reader manufactured in combination with the automated mini-incubator BioSpa 8 by BioTek provides the unique opportunity to capture, store and analyze live cell images in bright field, phase contrast and fluorescence.
Below are just a few examples of biological assays that can be performed using this equipment:
- Label-free or fluorescence-based cell proliferation analysis
- Label-free imaging and quantification of 3D spheroid-based tumor invasion
- assays
- Live cell imaging of multi-parametric cell death using high contrast bright field
- and fluorescence imaging
- Label-free imaging of 2D scratch wound healing assays
- Cell invasion assays
- Cell cycle analysis using DNA content and protein expression
- Cytation 5 is currently equipped with following filter sets:
- DAPI filter cube – Blue
- GFP filter cube – Green and Yellow
- RFP filter cube – Orange and Red
- Texas Red filter cube – Red
- CY5 filter cube – Far Red
Drug Discovery Core services & fees
Screening of chemical libraries
The timeline of a typical chemical library screening project can be roughly divided into three phases: preparation, library screening, and data analysis/hit selection/pickup.
We recommend scheduling a preliminary meeting early during the planning phase of your project to discuss estimated costs and assay requirements and controls for the high throughput format. By doing this early, you will save time and cost by avoiding unnecessary and repeated experiments later.
In the Links section of this website you will find general information about chemical screenings, requirements and evaluation of readouts to be used in high throughput screening and information about statistical analysis of readouts and HTS data. This information can be very helpful at the early stage of screening project planning.
To initiate the project please contact Dr. Katerina Gurova to schedule initial discussion of the project. Based on this discussion we will provide you with project summary and cost and time estimates.
All screening experiments should be scheduled (via email) at least one week in advance. If you need to cancel or reschedule for another day, please give us at least 24 hours’ notice (via email).
Handling of library plates will be performed only by shared resource staff members. The process of the library plate preparation is covered by the setup fee. The resource will provide 0.5 μl of primary hits for verification purposes at minimal cost. Reordering the compound for follow-up experiments can be done upon request (contact us for more information).
Original screening data will be stored on the resource computers. We guarantee the confidentiality of this data. In cases where sharing of the data could be beneficial, such as if the project could benefit from cross-referencing the data between different screenings, or the investigator using the facility would like to obtain data about similar or related screenings, sharing of screening information may be possible given the consent of all involved parties.
Additional services
Drug Discover Core can perform variety of cell-based experiments upon request. These experiments will be performed in high density format using our automated high precision equipment ensuring the highest level of accuracy and reproducibility. The results will be provided in the form of tables, charts, microscopic images and time lapse video.
- Label-free or fluorescent cell proliferation analysis
- Cell migration wound healing assay
- Cell invasion assay using porous membrane inserts
- Cell viability and toxicity analysis
- CC 50/IC 50 experiments
- Drug synergy analysis
Drug Discovery Core links
Equipment use
The Drug Discovery Core equipment can be used for non-screening projects by Roswell Park researchers for a minimal hourly fee (please contact Katerina.Gurova@RoswellPark.org for pricing information). Please note that screening projects will have a priority in equipment use, so check the availability before planning your experiments.
Please acknowledge the contributions of the SMS in oral presentations and publications. We appreciate receiving copies of relevant publications, as citations, PDF files or reprints.
Location and hours
Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer CenterSmall Molecule Screening Shared Resource
Center for Genetics and Pharmacology, Room L1-215
Elm and Carlton Streets
Buffalo, New York 14263
Monday – Friday, 8 a.m. – 5 p.m.
Drug Discovery Core faculty and staff
Henry Withers, PhD
Associate Director
Phone: 716-845-1300, x5258
Email: Henry.Withers@RoswellPark.org
Brian Buckley
Research Associate
Phone: 716-845-4697
Email: Brian.Buckley@RoswellPark.org
The Drug Discovery Core at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center provides investigators with easy access to the reagents, equipment and expertise needed during the early stages of a drug development project. This includes the design and adjustment of readouts, high throughput screening, hit selection and confirmation and preliminary hit characterization.
The collection of chemicals at the SMS totals more than 110,000 compounds. Our larger libraries are the EXPRESS-Pick (ChemBridge, Inc.) and HitDiscover (Maybridge-Thermo Fisher Scientific). These libraries contain 108,480 small drug-like molecules, while our smaller libraries of LOPAC (Sigma), Spectrum (MSD, Inc.) and Tocriscreen Total (Tocris Bioscience) contain 4,400 bioactive compounds with known properties. Our FDA-approved drug library (SelleckChem) contains 1508 compounds.
Sophisticated automated liquid handling equipment is used to ensure accurate delivery of these libraries in both 96- and 384- well format. The automated liquid handler JANUS (PerkinElmer) and high-density pin array allows accurate delivery of compounds in nL volumes with productivity of 20-25,000 data points per day.
Our versatile multilabel plate readers EnVision (PerkinElmer) and Cytation 5 (BioTek) allow for screens using either cell based or biochemical assays. Technology platforms that can be used in projects include fluorescence intensity, fluorescence polarization, FRET and TR-FRET, ALPHA-screen, flash and glow luminescence and live cell imaging in 2D and 3D cell culture.
Dedicated tissue culture equipment simplifies the procedure of cell preparation for cell-based readout systems and the plating of the cells in high density multi-well format.
Our tissue culture room is equipped with a laminar flow hood, CO2 incubators, water baths and automatic multichannel pipettors.
Drug Discovery Core selected publications
- Korotchkina L, Kazyulkin D, Komarov PG, Polinsky A, Andrianova EL, Joshi S, Gupta M, Vujcic S, Kononov E, Toshkov I, Tian Y, Krasnov P, Chernov MV, Veith J, Antoch MP, Middlemiss S, Somers K, Lock RB, Norris MD, Henderson MJ, Haber M, Chernova OB, Gudkov AV. OT-82, a novel anticancer drug candidate that targets the strong dependence of hematological malignancies on NAD biosynthesis. Leukemia. 2020 Jul;34(7):1828-1839.
- Yang X, Shen H, Buckley B, Chen Y, Yang N, Mussell AL, Chernov M, Kobzik L, Frangou C, Han SX, Zhang J. NTRK1 is a positive regulator of YAP oncogenic function. Oncogene. 2019 Apr;38(15):2778-2787
- Bailey DC, Buckley BP, Chernov MV, Gulick AM. Development of a High-Throughput Biochemical Assay to Screen for Inhibitors of Aerobactin Synthetase IucA. SLAS Discov. 2018 Dec;23(10):1070-1082.
- Azad T, Janse van Rensburg HJ, Lightbody ED, Neveu B, Champagne A, Ghaffari A, Kay VR, Hao Y, Shen H, Yeung B, Croy BA, Guan KL, Pouliot F, Zhang J, Nicol CJB, Yang X. A LATS biosensor screen identifies VEGFR as a regulator of the Hippo pathway in angiogenesis. Nat Commun. 2018 Mar 13;9(1):1061
- Gupta N, Badeaux M, Liu Y, Naxerova K, Sgroi D, Munn LL, Jain RK, Garkavtsev I. Stress granule-associated protein G3BP2 regulates breast tumor initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jan 31;114(5):1033-1038
- Wu W, Xu C, Ling X, Fan C, Buckley BP, Chernov MV, Ellis L, Li F, Muñoz IG, Wang X. Targeting RING domains of Mdm2-MdmX E3 complex activates apoptotic arm of the p53 pathway in leukemia/lymphoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2015 Dec 31;6(12):e2035
- Arginylation regulates purine nucleotide biosynthesis by enhancing the activity of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthase. Zhang F, Patel DM, Colavita K, Rodionova I, Buckley B, Scott DA, Kumar A, Shabalina SA, Saha S, Chernov M, Osterman AL, Kashina A. Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 15; 6:7517.
- Wei Luo, Wei-Dong Yu, Yingyu Ma, Mikhail Chernov, Donald L. Trump and Candace S. Johnson Inhibition of protein kinase CK2 reduces CYP24A1 expression and enhances 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 anti-tumor activity. Cancer Res. 2013 Apr 1; 73(7):2289-97.