Multicenter phase 2 study of tivozanib in advanced hepatocellular cancer (HCC)
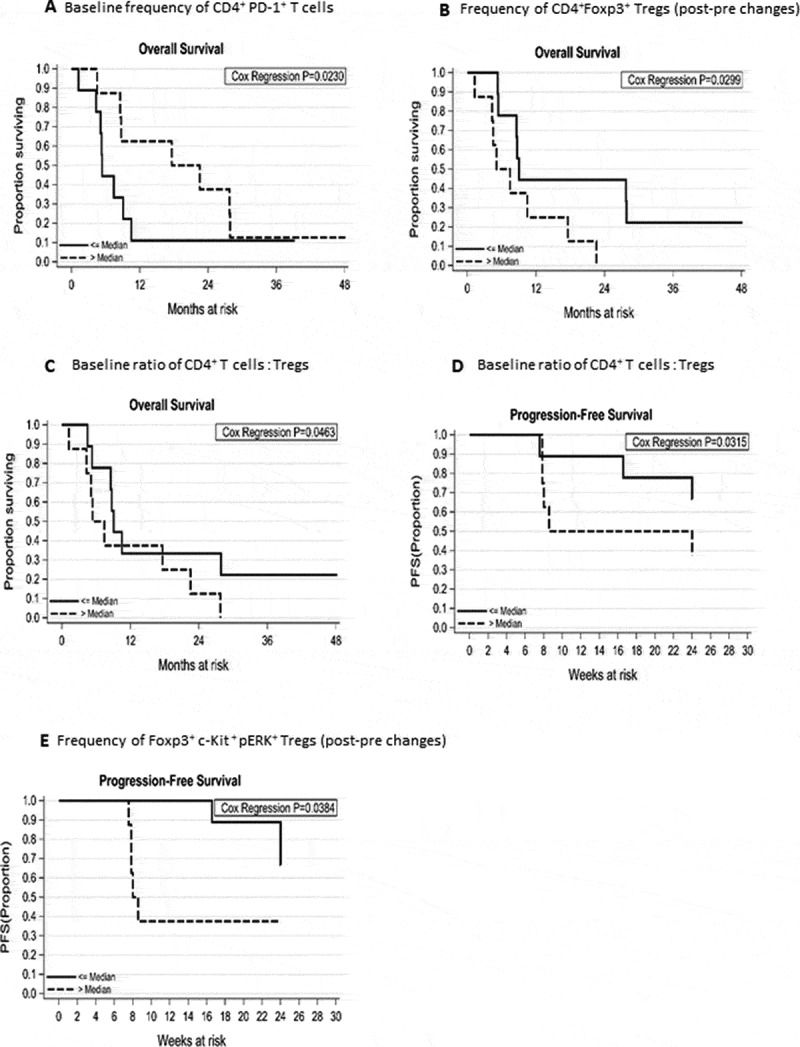
The immune modulatory effect of tivozanib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and the underlying immune mechanisms impacting survival of HCC patients have not been investigated. Pre-clinical studies have shown that tivozanib reduces Tregs and MDSCs accumulation through inhibition of c-Kit/SCF axis.
We rationalized that c-Kit/SCF axis antagonism by tivozanib may reverse tumor-induced immune suppression in HCC patients. The frequency of circulating Tregs, MDSCs, CTLA-4+Tregs, PD-1+T cells, c-Kit+pERK-2+Tregs, and c-Kit+pERK-2+MDSCs were quantified in HCC patients at baseline and two time points during tivozanib treatment.
We reported for the first time that reduction in Tregs after tivozanib treatment and increased levels of baseline CD4+PD-1+T cells correlated with significant improvement in overall survival (OS) of the patients and these signatures may be potential biomarkers of prognostic significance.
This immune modulation resulted from tivozanib-mediated blockade of c-Kit/SCF signaling, impacting ERK2 phosphorylation on Tregs and MDSCs. Low pre-treatment CD4+T cells: Treg ratio and reduction in the frequencies of Foxp3+c-Kit+pERK+Tregs after tivozanib treatment correlated significantly with progression free survival.
Read the research
- Kalathil SG, Wang K, Hutson A, Iyer R, Thanavala Y. Tivozanib mediated inhibition of c-Kit/SCF signaling on Tregs and MDSCs and reversal of tumor induced immune suppression correlates with survival of HCC patients. Oncoimmunology. 2020 Sep 30;9(1):1824863.
Granzyme B production as a biomarker for the immunomodulatory activity of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma (NCT02072486)
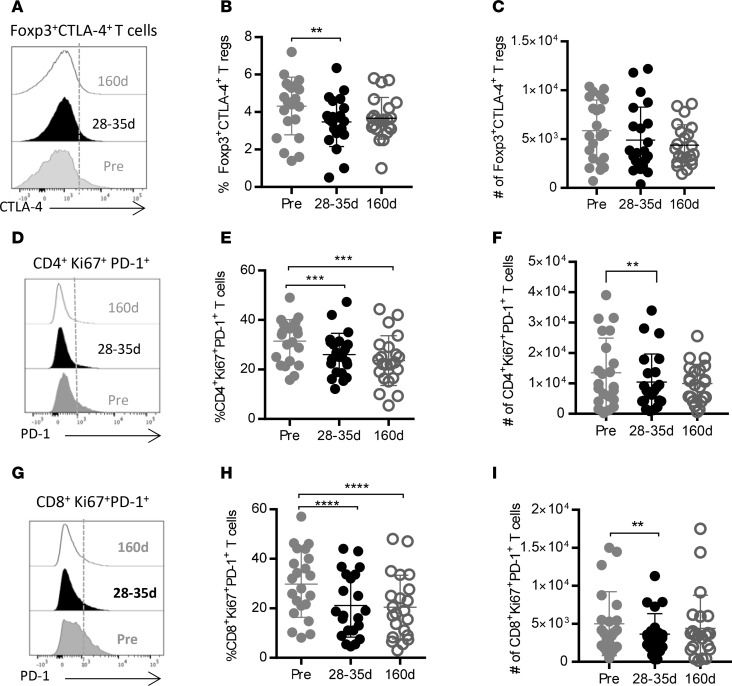
Sorafenib has been shown to reduce the extent of immunosuppression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The rationale of this investigation was to identify biomarkers that can predict treatment efficacy of sorafenib in HCC patients and to unravel the mechanism by which sorafenib impedes immune suppression mediated by distinct immunosuppressive cell subsets.
Elevated levels of CD8+Ki67+ T cells producing IFN-γ were associated with improved progression-free survival and overall survival (OS). High frequencies of these T cells were correlated with significantly reduced risk of death over time. Patients with an increased pretreatment T effector/Treg ratio showed significant improvement in OS. ERK+flt-3+ Tregs and MDSCs were significantly decreased after sorafenib therapy. Increased numbers of baseline flt-3+p-ERK+ MDSCs were associated with survival benefit of patients.
This study was funded by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Oncology Research Program.
Read the research
- Kalathil SG, Hutson A, Barbi J, Iyer R, Thanavala Y. Augmentation of IFN-γ+ CD8+ T cell responses correlates with survival of HCC patients on sorafenib therapy. JCI Insight. 2019 Aug 8;4(15):e130116.
- Kalathil SG, Lugade AA, Miller A, Iyer R, Thanavala Y. PD-1+ and Foxp3+ T cell reduction correlates with survival of HCC patients after sorafenib therapy. JCI Insight. 2016 Jul 21;1(11):e86182.
Immunogenicity in humans of an edible vaccine for hepatitis B
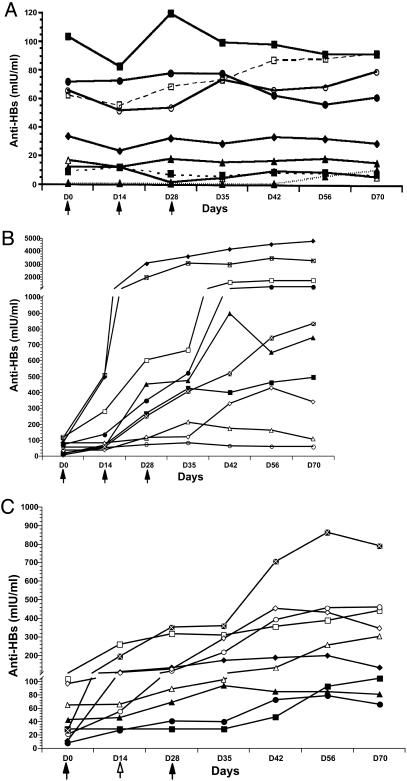
A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluated the immunogenicity of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) expressed in potatoes and delivered orally to previously vaccinated individuals. The potatoes accumulated HBsAg at approximately 8.5 microg/g of potato tuber, and doses of 100 g of tuber were administered by ingestion.
The correlate of protection for hepatitis B virus, a nonenteric pathogen, is blood serum antibody titers against HBsAg. After volunteers ate uncooked potatoes, serum anti-HBsAg titers increased in 10 of 16 volunteers (62.5%) who ate three doses of potatoes; in 9 of 17 volunteers (52.9%) who ate two doses of transgenic potatoes; and in none of the volunteers who ate nontransgenic potatoes.
These results were achieved without the coadministration of a mucosal adjuvant or the need for buffering stomach pH. We concluded that a plant-derived orally delivered vaccine for prevention of hepatitis B virus should be considered as a viable component of a global immunization program.
Read the research
- Thanavala Y, Mahoney M, Pal S, Scott A, Richter L, Natarajan N, Goodwin P, Arntzen CJ, Mason HS. Immunogenicity in humans of an edible vaccine for hepatitis B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Mar 1;102(9):3378-82.
- Thanavala Y, Yang YF, Lyons P, Mason HS, Arntzen C. Immunogenicity of transgenic plant-derived hepatitis B surface antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3358-61.
Connect with the Thanavala Lab
Department of Immunology
Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center
Elm and Carlton Streets
Buffalo, NY 14263