Cancers in the bile ducts or gallbladder are considered types of biliary cancer
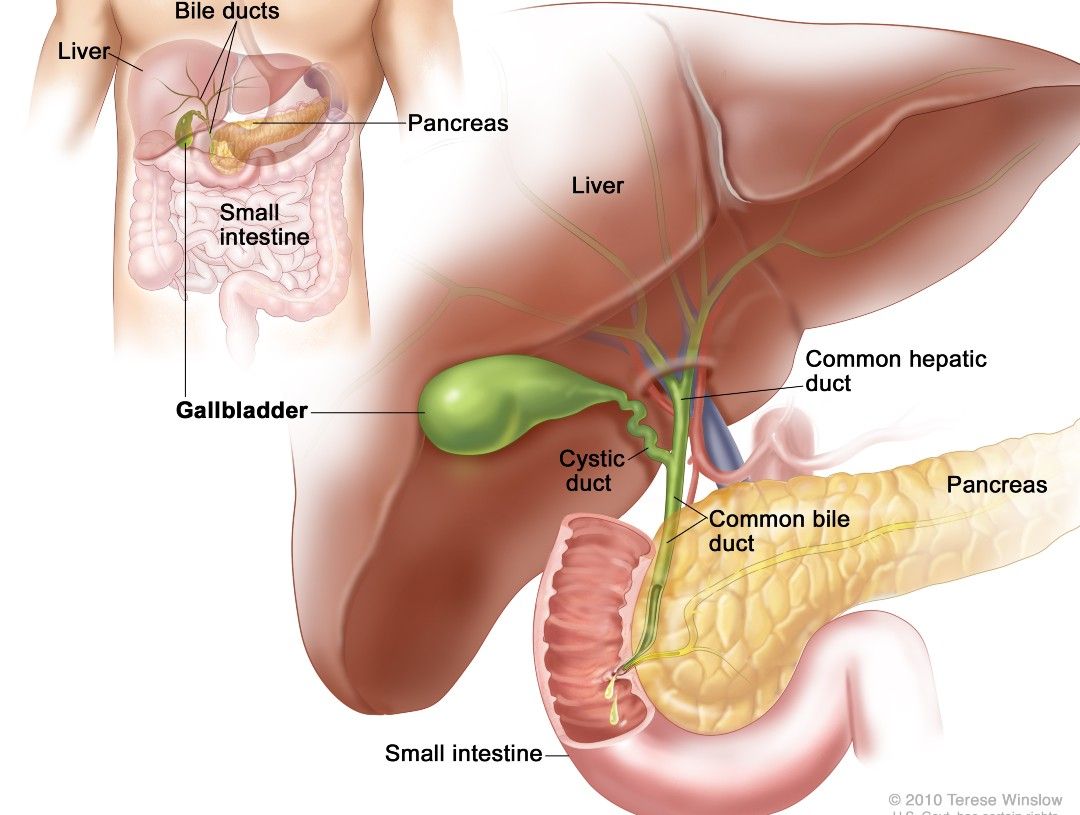
Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ lying beneath the liver that collects and stores bile (a fluid necessary for digestion of fats) that your liver produces. As the liver makes bile, it flows through the bile ducts, a network of tubes that converge and lead to the small intestine to help with digestion, or to the gallbladder to store for later use. When bile is needed, it’s released from the gallbladder to flow through the cystic duct to the common bile duct and on to the small intestine. The gallbladder and bile ducts together make up your biliary system.
About 11,900 new cases of biliary cancer are diagnosed in the U.S. each year and 4 in 10 of those are gallbladder cancer.
What is cholangiocarcinoma?
Cholangiocarcinoma is cancer in the bile ducts, and occurs when cells in any of the ducts become malignant. Bile duct cancers are described by the location of the bile ducts where it began.
Extrahapatic cholangiocarcinoma
Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma refers to cancer in the bile ducts that are outside of the liver, such as these cancer types:
- Hilar bile duct cancer (also called Klatskin tumor) occurs in the common hepatic duct, where all the ducts within the liver converge to exit the liver.
- Distal bile duct cancer occurs in the common bile duct which carries bile leaving the gallbladder through the cystic duct and from the common hepatic duct to the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine.
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Cancer that occurs in the branches of bile ducts within the liver are called intrahepatic.
What is gallbladder cancer?
Gallbladder cancer occurs when cells in the gallbladder begin to grow abnormally and out of control, called malignant. The gallbladder is made of three main layers of tissue:
- mucosal (inner) layer
- muscularis (middle) layer
- serosal (outer) layer
Gallbladder cancer typically begins in the innermost, mucosal layer and spreads outward as it grows.
What is papillary adenocarcinoma?
Papillary cancer occurs when the cancer cells grow into finger-like projections. Although this growth type is very rare, they are less likely to spread to the liver or lymph nodes, and have a better prognosis.
Rare cancer types
Other rare types of cancer may also begin in the biliary system. For example, sarcoma, adenosquamous carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma may occur (very rarely) in the gallbladder.
How are biliary cancers diagnosed? Get a second opinion
The Roswell Park Advantage — Liver and Pancreas Tumor Center
The gallbladder and bile ducts are intricately connected — physically and in their function — to your liver and pancreas. Cancers in these important organs, called hepatopancreaticobiliary (HPB) cancers, are rare and complex and require unique expertise from different medical specialties. At Roswell Park, these specialists are brought together in one center dedicated to caring for patients with HPB cancers, to provide not only the best possible treatments, but to do so in the optimal sequence and coordination that benefits patient survival and quality of life.