What we do
The Flow & Immune Analysis Shared Resource (FIASR) provides a comprehensive array of cutting-edge technologies on a variety of platforms including flow and image cytometry, proteomics, metabolomics, and spatial profiling techniques in support of Roswell investigators. The FIASR is recognized by the International Society for the Advancement of Cytometry (ISAC) for operational excellence and adherence to best practices. The Shared Resource is committed to expanding access to unique technologies and the use of advanced instrumentation, while maintaining an active program to educate the scientific community on innovative applications.
Quick links
Instruments
Helpful links
- Analysis software
- New accounts
- Education
- Meet our team
- Core grant citation
- Facility data for grants
- DeNovoSoftware (FCS Express)
- Panel design and spectral viewers
- Cytometry Societies
Flow cytometry analyzers
The flow cytomety analyzers are available 24/7 to trinaed users by reserving time on the FOM calendar.
- 3L, 16 fluorescent parameters with 2 scatter parameters
- High Throughput Sampler (96 well plate) option)
Laser | Bandpass Filter | Common Fluors (list is not exhaustive) |
|---|---|---|
405 nm violet laser | V450/50 | BV421, BV480, DAPI, Pacific Blue, V450, EF450, SB436, AF405, LD Violet |
V525/50 | BV510, V500, AmCyan, LD Aqua | |
V560/20 | Qdot565, BV570 | |
V585/15 | BV570 | |
V610/20 | BV605 | |
V660/20 | BV650 | |
V710/50 | BV711 | |
V780/60 | BV750, BV786, BV785 | |
488 nm blue laser | B530/30 | FITC, BB515, GFP, AF488, CFSE |
B575/26 | PE, mOrange, AF568 | |
B610/20 | PECF594, PEAF610, PEDazzle594, PEeFluor610, ECD, PI | |
B695/40 | PerCPCy5.5, BB700, PerCP, PECy5, PECy5.5 7AAD, PEeFluor710 | |
B780/60 | PECy5, PEAF750 | |
640 nm red laser | R670/14 | APC, AF647 |
R730/45 | AF700, APC-R700, DRAQ5 | |
R780/60 | APC-Cy7, APC-AF750, APCH7 |
- 4L, 18 fluorescent parameters with 2 scatter parameters
- High Throughput Sampler (96 well plate) option
Laser | Bandpass Filter | Common Fluors (list is not exhaustive) |
|---|---|---|
355 nm UV laser | U379/28 | BUV395, Indo-1 |
U460/14 | DAPI, Hoechst 33342, LD Blue, Zombie UV | |
U740/35 | BUV737 | |
405 nm violet laser | V450/50 | BV421, BV480, DAPI, Pacific Blue, V450, EF450, SB436, AF405, LD Violet |
V525/50 | BV510, V500, AmCyan, LD Aqua | |
V585/15 | BV570 | |
V610/20 | BV605 | |
V660/20 | BV650 | |
V710/50 | BV711 | |
V780/60 | BV750, BV786, BV785 | |
488 nm blue laser | B530/30 | FITC, BB515, GFP, AF488, CFSE |
B575/26 | PE, mOrange, AF568 | |
B610/20 | PECF594, PEAF610, PEDazzle594, PEeFluor610, ECD, PI | |
B695/40 | PerCPCy5.5, BB700, PerCP, 7AAD | |
B780/60 | PECy7, PEAF750 | |
640 nm red laser | R670/14 | APC, AF647 |
R730/45 | AF700, APC-R700, DRAQ5 | |
R780/60 | APC-Cy7, APC-AF750, APCH7 |
- 4L, 18 fluorescent parameters with 2 scatter parameters
Laser | Bandpass Filter | Common Fluors (list is not exhaustive) |
|---|---|---|
355 nm UV laser | U379/28 | BUV395, Indo-1 |
U460/14 | DAPI, Hoechst 33342, LD Blue, Zombie UV | |
U740/35 | BUV737 | |
405 nm violet laser | V450/50 | BV421, BV480, DAPI, Pacific Blue, V450, EF450, SB436, AF405, LD Violet |
V525/50 | BV510, V500, AmCyan, LD Aqua | |
V585/15 | BV570 | |
V610/20 | BV605 | |
V670/30 | BV650 | |
V710/50 | BV711 | |
V780/60 | BV750, BV786, BV785 | |
488 nm blue laser | B530/30 | FITC, BB515, GFP, AF488, CFSE |
B575/26 | PE, mOrange, AF568 | |
B610/20 | PECF594, PEAF610, PEDazzle594, PEeFluor610, ECD, PI | |
B710/50 | PerCPCy5.5, BB700, PerCP, PECy5, PECy5.5, 7AAD, PEeFluor710 | |
B780/60 | PECy7, PEAF750 | |
640 nm red laser | R670/30 | APC, AF647 |
R710/50 | AF700, APC-R700, DRAQ5 | |
R780/60 | APC-Cy7, APC-AF750, APCH7 |
- 5L, 23 fluorescent parameters with 2 scatter parameters
- High Throughput Sampler (96 well plate) option
Laser | Bandpass Filter | Common Fluorescent Tags (list is not exhaustive) |
|---|---|---|
349 nm UV laser | UV379/29 | BUV395, Spark UV 387, SBUV400 |
UV515/30 | DAPI, BUV496, LD Blue, Zombie UV, SBUV510 | |
UV586/15 | BUV563, SBUV575, cFluor UV570 | |
UV673/30 | BUV661, SBUV665, cFluor UV670 | |
UV740/35 | BUV737, SBUV740, cFluor UV740 | |
UV820/60 | BUV805, SBUV795, cFluor UV790 | |
405 nm UV laser | V431/28 | BV421, Pacific Blue, V450, EF450, SB436, AF405, LD Violet |
V525/30 | BV510, V500, AmCyan, Pac Orange, LD Aqua | |
V610/20 | BV605, SBV600, cFluor V605, cFluor V610 | |
V670/30 | BV650 | |
V710/50 | BV711, SBV702, cFluor V715 | |
V780/60 | BV750, BV786, BV785, SBV780, cFluor V780 | |
488 nm blue laser | B515/20 | FITC, BB515, GFP, AF488, cFluor B532, CFSE |
B610/20 | BB630, RB613, NovaBlue610 | |
B710/50 | PerCPCy5.5, BB700, PerCP, RB670, cFluor B690 | |
B780/60 | BB790, RB780, NovaBlue 760, NovaBlue 800 | |
561 nm yellow/green laser | YG586/15 | PE, RFP, tdTomato AF568, BYG584, cFluor BYG575 |
YG610/20 | PECF594, PEDazzle594, PEeFluor610, PI, mCherry | |
YG670/30 | PECy5, PECy5.5, NovaYellow 690, 7AAD | |
YG780/60 | PECy7, NovaYellow 810, cFluor BYG781 | |
637 nm red laser | R670/14 | APC, AF647, cFluor R659, LD Far Red |
R730/45 | AF700, APC-R700, cFluor R720 | |
R780/60 | APC-Cy7, APC-AF750, APCH7, cFluor R780 |
- 5L, 64 detectors, 40+ fluorescent parameters with 3 scatter parameters (FSC (488nm), SSC (405nm), SSC-B (488nm)
- Aurora C has High Throughput Sampler (96 well plate or 40 tube) option
Laser | Channel | Bandpass Filter | Common Fluors (list is not exhaustive) |
|---|---|---|---|
355 nm UV laser | UV1 | NUV373/15 | |
UV2 | NUV388/15 | BUV395 | |
UV3 | NUV428/15 | ||
UV4 | NUV443/15 | ||
UV5 | NUV458/15 | ||
UV6 | NUV473/15 | ||
UV7 | NUV542/28 | BUV496 | |
UV8 | NUV542/28 | ||
UV9 | NUV582/31 | BUV563 | |
UV10 | NUV613/31 | ||
UV11 | NUV664/27 | BUV661 | |
UV12 | NUV692/28 | ||
UV13 | NUV720/29 | BUV737 | |
UV14 | NUV750/30 | ||
UV15 | NUV780/30 | ||
UV16 | NUV812/34 | BUV805 | |
405 nm violet laser | V1 | V428/15 | BV421 |
V2 | V443/15 | AF405, SB436 | |
V3 | V458/15 | PacBlue, eFluor450 | |
V4 | V473/15 | BV480 | |
V5 | V508/20 | eFluor506 | |
V6 | V525/17 | ||
V7 | V542/17 | BV510 | |
V8 | V581/19 | BV570, PacOrange | |
V9 | V598/20 | ||
V10 | V615/20 | BV605, SB600 | |
V11 | V664/27 | BV650, SB645 | |
V12 | V692/28 | ||
V13 | V720/29 | BV711, SB702 | |
V14 | V750/30 | BV750 | |
V15 | V780/30 | BV785, BV786 | |
V16 | V812/34 | ||
488 nm blue laser | B1 | B508/20 | BB515 |
B2 | B525/17 | FITC, AF488 | |
B3 | B542/17 | AF532 | |
B4 | B581/19 | ||
B5 | B598/20 | ||
B6 | B615/20 | ||
B7 | B661/17 | ||
B8 | B679/18 | PerCP | |
B9 | B697/19 | BB700, PerCPCy5.5 | |
B10 | B717/20 | PerCP-eFluor710 | |
B11 | B738/21 | ||
B12 | B760/23 | ||
B13 | B783/23 | ||
B14 | B812/34 | ||
561 nm yellow/green laser | YG1 | YG577/20 | PE |
YG2 | YG598/20 | ||
YG3 | YG615/20 | PEDazzle594, PECF594, PE-AF610, PE-eFluor610 | |
YG4 | YG661/17 | ||
YG5 | YG679/18 | PECy5 | |
YG6 | YG697/19 | ||
YG7 | YG720/29 | PECy5.5, PE-AF700 | |
YG8 | YG750/30 | ||
YG9 | YG780/30 | PECy7 | |
YG10 | YG812/34 | ||
638 nm red laser | R1 | R661/17 | APC |
R2 | R679/18 | AF647, eFluor660 | |
R3 | R697/19 | ||
R4 | R717/20 | AF700, APC-R700 | |
R5 | R738/21 | ||
R6 | R760/23 | ||
R7 | R783/23 | APCCy7, APCH7, APC-AF750, APCFire750 | |
R8 | R812/34 |
Fluorochrome | Filter available |
|---|---|
Calcium Flux | 405/20 |
Side Population | 645LP |
YFP | 546/20 |
Imaging flow cytometers
- 5L, up to 10 fluorescent parameters with two brightfield images
- 12 channel, 2 camera instrument
- Side scatter in channel 6 or channel 12 (dedicated 785nm scatter laser)
- 20x, 40x, 60x magnification
- Extended Depth of Field (EDF, 16 µ) and autosampler option (96-well plate format)
Camera 1 | Bandpass Filter | Common Fluors (list is not exhaustive) |
|---|---|---|
488 nm blue | Ch1: 420-480 nm | Brightfield |
Ch2: 480-560 nm | FITC, BB515, GFP, AF488, CFSE | |
Ch3: 560-595 nm | PE, AF568 | |
Ch4: 595-642 nm | PECF594, PEAF610, PEDazzle594, PEeFluor610, ECD, AF594 | |
Ch5: 642-745 nm | PerCPCy5.5, BB700, PerCP, PECy5, PECy5.5, 7AAD, PEeFluor710 | |
Ch6: 745-800 nm | PECy7, PEAF750 | |
Camera 2 | Bandpass Filter | |
405 nm violet | Ch7: 420-505 nm | BV421, BV480, DAPI, Pacific blue, V450, LD Violet |
Ch8: 505-570 nm | BV510, V500, AmCyan, LD Aqua | |
Ch9: 570-595 nm | Brightfield | |
Ch10: 595-642 nm | BV605 | |
Ch11: 642-745 nm | AF647, APC | |
Ch12: 745-800 nm | APC-Cy7, APC-AF750, APCH7 |
- 4L, up to 10 fluorescent parameters with two brightfield images
- 12 channel, 2 camera instrument
- Side scatter in channel 6 or channel 12 (dedicated 785nm scatter laser)
- 20x, 40x, 60x magnification
Camera 1 | Bandpass Filter | Common Fluors (list is not exhaustive) |
|---|---|---|
488 nm blue | Ch1: 420-480 nm | Brightfield |
Ch2: 480-560 nm | FITC, BB515, GFP, AF488, CFSE | |
Ch3: 560-595 nm | PE, AF568 | |
Ch4: 595-642 nm | PECF594, PEAF610, PEDazzle594, PEeFluor610, ECD, AF594 | |
Ch5: 642-745 nm | PERCPCy5.5, BB700, PerCP, PECy5, PECy5.5, 7AAD, PEeFluor710 | |
Ch6: 745-800 nm | PECy7, PEAF750 | |
Camera 2 | Bandpass Filter | |
405 nm violet | Ch7: 420-505 nm | BV421, BV480, DAPI, Pacific blue, V450, LD Violet |
Ch8: 505-570 nm | BV510, V500, AmCyan, LD Aqua | |
Ch9: 570-595 nm | Brightfield | |
Ch10: 595-642 nm | BV605 | |
Ch11: 642-745 nm | AF647, APC | |
Ch12: 745-800 nm | APC-Cy7, APC-AF750, APCH7 |
Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
FIASR has two cell sorters in a BSL2+ facility. One is available for operator-assisted sorting and the other is available for use 24/7 to trained users by reserving time on the FOM calendar.
Operator assisted sorting: Researchers bring stained single cell suspensions to the Resource with controls, buffers, and collection tubes. Together with the operator, the experiment is set up and sort logic is defined. After setup, researchers will not need to be present for the remainder of the sort.
New sorts: Submit the online Sort Information form to request time. The FACS operators will contact you to confirm your appointment and to discuss specifics.
Repeat sorts: Submit the short Sort Appointment Request form to request time. FACS operators will contact you to finalize the appointment details.
Appointments are not guaranteed until confirmed and entered in FOM.
Researchers can refer to “Guidelines to Sorting” for more detailed information.
Contact Information:
Please email Xiaojun Liu (Xiaojun.Liu@RoswellPark.org) or Jennifer Chinnici (Jennifer.Chinnici@RoswellPark.org).
- 5L, 23 fluorescent parameters with 2 scatter parameters (identical to Symphony A3)
- Nozzle options : 70 um (70 psi), 85 um (45 psi), 100 um (20 psi), 130 um (13 psi)
- Sort options : 6-way 5 mL or 1.5 mL tube sort, 4-way 15 mL tube sort, plate sorts (6 - 384 well plates), slides
Laser | Bandpass Filter | Common Fluorescent Tags (list is not exhaustive) |
|---|---|---|
349 nm UV laser | UV379/28 | BUV395, Spark UV 387, SBUV400 |
UV515/30 | DAPI, BUV496, LD Blue, Zombie UV, SBUV510 | |
UV586/15 | BUV563, SBUV575, cFluor UV570 | |
UV670/30 | BUV661, SBUV665, cFluor UV670 | |
UV740/35 | BUV737, SBUV740, cFluor UV740 | |
UV820/60 | BUV805, SBUV795, cFluor UV790 | |
405 nm UV laser | V430/28 | BV421, Pacific Blue, V450, EF450, SB436, AF405, LD Violet |
V525/50 | BV510, V500, AmCyan, Pac Orange, LD Aqua | |
V610/20 | BV605, SBV600, cFluor V605, cFluor V610 | |
V670/30 | BV650 | |
V710/50 | BV711, SBV702, cFluor V715 | |
V780/60 | BV750, BV786, BV785, SBV780, cFluor V780 | |
488 nm blue laser | B515/20 | FITC, BB515, GFP, AF488, cFluor B532, CFSE |
B610/20 | BB630, RB613, NovaBlue610 | |
B710/50 | PerCPCy5.5, BB700, PerCP, RB670, cFluor B690 | |
B780/60 | BB790, RB780, NovaBlue 760, NovaBlue 800 | |
561 nm yellow/green laser | YG586/15 | PE, RFP, tdTomato AF568, BYG584, cFluor BYG575 |
YG610/20 | PECF594, PEDazzle594, PEeFluor610, PI, mCherry | |
YG670/30 | PECy5, PECy5.5, NovaYellow 690, 7AAD | |
YG780/60 | PECy7, NovaYellow 810, cFluor BYG781 | |
637 nm red laser | R670/30 | APC, AF647, cFluor R659, LD Far Red |
R710/50 | AF700, APC-R700, cFluor R720 | |
R780/60 | APC-Cy7, APC-AF750, APCH7, cFluor R780 |
- 4L, 13 fluorescent parameters with 2 scatter parameters (similar to Fortessa B and C)
- Sheath pressure is adjustable from 2 to 75 psi
- Nozzle sizes 100 micron (85 and 130 micron also available)
- Sort options: 4-way tube sort, plate sorts (6, 12, 24, 48, 96, 384 well plates)
Laser | Bandpass Filter | Common Fluors (list is not exhaustive) |
|---|---|---|
355 nm UV laser | U379/28 | BUV395, Indo-1 |
U460/14 | DAPI, Hoechst 33342, LD Blue, Zombie UV | |
405 nm violet laser | V450/50 | BV421, BV480, DAPI, Pacific Blue, V450, EF450, SB436, AF405, LD Violet |
V530/30 | BV510, V500, AmCyan, LD Aqua | |
488 nm blue laser | B530/30 | FITC, BB515, GFP, AF488, CFSE |
B575/25 | PE, mOrange, AF568 | |
B610/20 | PECF594, PEAF610, PEDazzle594, PEeFluor610, ECD, PI | |
B710/50 | PerCPCy5.5, BB700, PerCP, PECy5, PECy5.5, 7AAD, PEeFluor710 | |
B780/60 | PECy7, PEAF750 | |
640 nm red laser | R660/20 | APC, AF647 |
R730/30 | AF700, APC-R700, DRAQ5 | |
R780/60 | APC-Cy7, APC-AF750, APCH7 |
- Available 24/7 to trained users by reserving time on the FOM calendar
- 4L–colinear for 488/561 nm laser lines and 405/638 nm laser lines
- 12 fluorescent and 2 scatter parameters
- Available nozzle sizes: 70, 100, and 130 micron
- Sort options: 4-way tube sort, plate sorts (6, 12, 24, 48, 96, 384 well plates)
Laser | Bandpass Filter | Common Fluors (list is not exhaustive) |
|---|---|---|
488 nm blue laser | 525/50 | FITC, BB515, GFP, AF488, CFSE |
585/30 | PE, mOrange, AF568 | |
617/30 | PECF594, PEAF610, PEDazzle594, PEeFluor610, ECD, PI | |
695/50 | PerCPCy5.5, BB700, PerCP, PECy5, PECy5.5, 7AAD, PEeFluor710 | |
785/60 | PECy7, PEAF750 | |
405 nm violet laser | 450/50 | BV421, BV480, DAPI, Pacific blue, V450, EF450, SB436, AF405, LD Violet |
525/30 | BV510, V500, AmCyan, LD Aqua | |
585/30 | BV570 | |
617/30 | BV605 | |
665/30 | APC, AF647, BV650 | |
720/60 | AF700, APC-R700, DRAQ5 | |
785/60 | APC-Cy7, APC-AF750, APCH7, BV785, BV786 |
Slide-based immune profiling/imaging
The Phenocycler Fusion is an automated immunofluorescence-based analyzer that performs cyclic visualization of 3 immuno-fluorescent analytes at a time. This process can be repeated multiple times and the simultaneous detection of over 100 immunofluorescent probes have been reported. This imaging process is applicable to FFPE and cryosections of human and mouse origin. A catalogue of pre-validated antibodies is available at The Spatial Biology Company | Akoya Biosciences. Custom conjugation of antibodies to targets not available through the catalog is also available. Instrument use is restricted to FIASR personnel only. For more information on the technology or to schedule an experiment please contact Orla Maguire (Orla.Maguire@RoswellPark.org) or Hans Minderman (Hans.Minderman@RoswellPark.org).
Live cell imaging
xCelligence-MP (Agilent)
The Agilent xCELLigence real-time cell analysis (RTCA) multiple plates (MP) system provides a unique and powerful means to monitor cells in real time, without the potential artifacts generated by using labels. This noninvasive measurement allows detection of changes in adherence, morphology, and viability without the need for overexpression of reporter and target proteins. This provides physiologically relevant data throughout the entire experiment.
This instrument is currently housed in an incubator in Dr. Brentjens department on the 5th floor of the Cancer Cell Center. Training and calendar access requests should be discussed with Dr. Terence Purdon (Terence.Purdon@RoswellPark.org).
Plates used for the instrument are available from FIASR upon request at $66 each. Please email FICSR@RoswellPark.org to arrange pickup.
Proteomic analyzers
The xMAP INTELLIFLEX® System is a flow-bead multiplex analyzer that can perform up to 500 tests in a single reaction volume using magnetic beads to capture soluble analytes from plasma, serum, and tissue culture supernatants.
The Luminex® 200™ System is an older version of the Intelliflex technology that can perform up to 100 tests in a single reaction volume. Multiplexing kits for both instruments are commercially available from several vendors, including Millipore, BioRad, ThermoFisher, and R&D Systems, with assays for many different species and sample types.
New Assay Requests: Contact Nitika Sharma (Nitika.Sharma@RoswellPark.org) to discuss project specifics.
The Isolight analyzer from Isoplexis/Bruker performs automated highly mutliplexed live single cell secretome analysis, single cell highly multiplexed phosphoproteomic and metabolic analysis as well as bulk/population protein analysis all on one platform and in a single workflow. Fully analyzed data can be obtained within 24 hours. IsoLight is ideal for comprehensive profiling of the secretory capabilities of different cell types and of cells at different developmental or treatment stages. Click on the links to browse the commercially available analyte human and murine panels for bulk (Codeplex) or single cell (Isocode) analysis.
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot (ELISpot) quantitatively measures the frequency of cytokine secretion for a single cell. A plate is coated with antibodies for the cytokine of interest. T cells are added with/without stimuli. The coating antibody captures the secreted cytokine and a second cytokine-specific antibody is coupled to a chromogenic substrate and used for detection. Results appear as spots, with each spot corresponding to one cytokine-secreting cell. The number of spots equals the number of cytokine-secreting cells for a specific antigen. The modified FluoroSpot assay uses a fluorescently tagged antibody instead of a biotin-streptavidin substrate system.
FIASR has the CTL S6 FluoroCore Analyzer that can also perform PBMC counting. The FluoroCore is equipped with optics and an extra fluorescent channel which, along with CTL’s dedicated LDA Cell Counting Suite, can count dozens of PBMC samples within minutes, including the documentation of viability, and the calculation of resuspension volumes.
CTL provides several kits for the reader in FIASR (one color kits).
- 1 laser (488 nm) with 520 bandpass filter (FITC, Alexa Fluor® 488, Acridine Orange, sfGFP, GFP, Yo-Pro™, CFSC, Sytox™ Green)
- 96- or 384-well plate and Strip plate in 96 well format
- Single-color FluoroSpot analysis for precise quantification of per-cell secreted analyte via the HDR imaging feature
- Serves as a high-throughput reader for cell-mediated cytotoxicity assays
- FCS standard data output
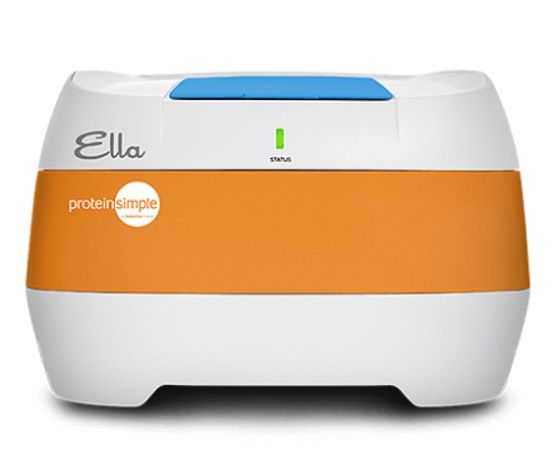
The ELLA automated immunoassay system performs immunoassays in a microfluidic Simple Plex cartridge, allowing researchers to acquire highly reproducible validated assay data with very few manual steps, and is the only self-contained testing platform for the simultaneous execution of multiple ELISA-based immunoassays.
Once a sample is loaded, it runs through a microfluidic channel that binds the protein of interest. Next, Ella washes off unbound analyte and adds a detection reagent. Because each channel has three Glass Nano Reactors (GNRs) coated with a capture antibody, you will get triplicate answers for each sample. Answers are then generated from the factory-calibrated standard curve that comes with every cartridge.
The assay volume required is 25 μL or less for up to 4-plex customized assays and the data is ready in two hours from sample prep. Cartridges are available ready-to-use or customizable at Bio-Techne.
Metabolic analyzers
Seahorse XFe96 extracellular flux analyzer tracks and records the oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) that reflects mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis in real-time in 96-well plate format.
Validated assays include the glycolysis stress test, cell mito stress test, mito fuel flex test, glycolytic rate assay, ATP rate assay, cell energy phenotype test and fatty acid oxidation measurement. Custom-made assays are also available. All kits can be viewed at Agilent.
Normalization of Seahorse data can be facilitated by in-situ cell counting using the BioTek Cytation 5, requiring no additional sample processing. Cytation 5 is a multichannel cell imaging platform capable of automated cell counting from fluorescently labeled nuclear images following the injection of cell permeable dye such as Hoechst 33342 via the Seahorse system. The instrument also performs high-contrast brightfield imaging, capturing whole-well images to provide visual feedback and quality control of cell seeding conditions.
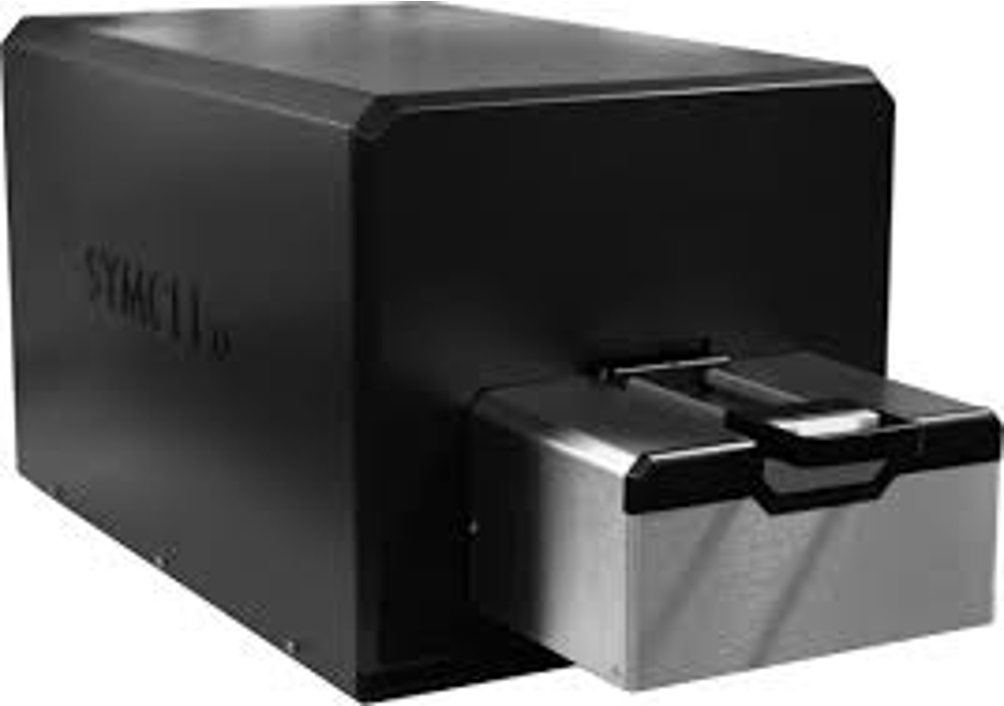
The Symcel calScreener™ measures the total metabolic activity of a sample, in real-time, and in unlimited run-time that can be set from hours to months. The calScreener directly measures the heat produced as a result of metabolic processes in the sample; the energy output is measured in μW.
The calScreener is a new addition to FIASR (June 2024) and we welcome any studies to test out the instrument. Contact Orla Maguire (Orla.Maguire@RoswellPark.org) or Wei Luo (Wei.Luo@RoswellPark.org) for more information.
Small particle analyzer
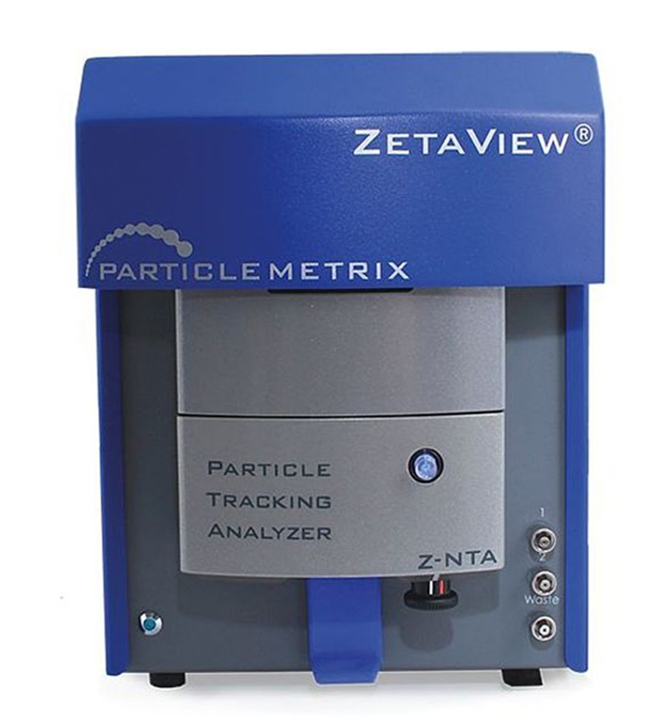
The ZetaView small particle analyzer employs Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) which relates the rate of Brownian motion of the particles in liquid suspension to particle size. The ZetaView NTA measures the size distribution profile of small particles approximately 10-1000 nanometers (nm) in suspension. The ZetaView is also capable of measuring the zeta-potential of the particles which is a measure of the electric charge on the nanoparticle surface.
The primary application of the NTA analysis at Roswell Park is measurement of extracellular vesicles (EV) and exosomes, cell-derived vesicles with a diameter between 30 and 100 nm.
The ZetaView analyzers are equipped with either a 488nm or 405nm laser to detect fluorescent particles if desired.
The ZetaView instruments are available 24/7 to trained users by reserving time on the FOM calendar.
Interested researchers should contact our principal operator Nitika Sharma (Nitika.Sharma@RoswellPark.org) or Hans Minderman (Hans.Minderman@Roswellpark.org) for project consultation and to discuss full service or training opportunities.
Analysis software
- FCS Express 7.0: Roswell Park has a network license free for all Roswell employees. Order software through ServiceNow.
- FlowJo 10: FIASR has 2 workstations with FlowJo that are available for use during business hours. Individual PIs are responsible for purchasing their own licenses if desired.
- WinList 9.0: Roswell Park has a network license free for all Roswell employees. Contact Joseph Hanson to arrange access.
- Modfit 4.0: Roswell Park has a network license free for all Roswell employees. Contact Joseph Hanson to arrange access.
- OMIQ: Roswell has several single seat licenses available for Roswell employees. Inquiries can be made to Hans Minderman.
- IDEAS 6.2 (Amnis): FIASR has a license free for all Roswell employees.
- Amnis AI: Amnis AI works with the IDEAS 6.3 analysis software to help researchers classify objects using computer-aided tagging and AI algorithms. FIASR has one workstation with Amnis AI and IDEAS v6.3, access is available for use during business hours. Inquiries can be made to Hans Minderman.
- Image Pro Plus 6.3: Image Pro Plus 6.3 is an advanced image analysis software. It accepts a wide variety of image file formats. FIASR has one seat license available for use during business hours.
- ImageJ: ImageJ is a Java-based free-ware image analysis package developed at the National Institutes of Health. Roswell employees can order the software through ServiceNow.
New accounts
FIASR uses FOM (Facility Online Manager) as an integrated calendar, instrument sign-on, and billing system. Every new user will need to set up an individual account in FOM.
Each lab (or company) will also need a group account for logging in to the computer software on our analyzer instruments. Only one account will be created per PI. For more information on new accounts, contact Orla Maguire.
Education
FIASR staff teach several free courses to educate the Roswell Park and Buffalo community on the techniques employed in our shared resource. Classes typically take about one - three hours.
MANDATORY: Introduction to Flow Cytometry: Didactic 1.5hr class introducing the basics of flow cytometry, experimental design, analysis, and outlining the rules to follow when in FIASR.
Three 2-hour one-on-one instrument training sessions include:
- Initial training using our validated samples
- Researcher brings their own samples
- Troubleshooting and reenforcing correct procedures
For those instruments that are available 24/7, an additional training session with FIASR staff is required for after-hours access.
Other optional classes are offered according to demand. Drs. Minderman and Maguire also teach the graduate course RPG564 Principles of Flow and Image Cytometry in the Fall semester open to all graduate students and available to audit is space permits.
Contact Orla Maguire (Orla.Maguire@RoswellPark.org) for more information.
Meet our team
Location & hours
Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center
Flow & Immune Analysis Shared Resource
Elm and Carlton Streets
Buffalo, New York 14263
Location: Cancer Cell Center 3rd floor
General lab phone: 716-845-3470
General lab email: FICSR@RoswellPark.org
Grant information
Please acknowledge the Flow & Immune Analysis Shared Resource in your publication as follows:
Cytometry services were provided by the Flow & Immune Analysis Shared Resource at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, supported in part by the NCI Cancer Center Support Grant NCI P30CA016056 and NCI R50 R50CA211108.
If you are using the ImageStream imaging flow cytometer in your publications, please acknowledge the Shared Instrument grant that funded the acquisition of this instrument as follows:
The ImagestreamX-MKII instrument was funded through the NIH Shared Instrument Grant S10OD018048.
If you are using the SONY MA900 in your publications, please acknowledge the Shared Instrument grant that funded the acquisition of this instrument as follows:
The SONY MA900 sorter was funded through the NIH Shared Instrument Grant S10OD025183.
The Flow & Immune Analysis Shared Resource (FIASR) at the Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center provides a comprehensive array of cutting- edge technologies on a variety of platforms including flow and image cytometry, proteomics, metabolomics, and spatial profiling techniques in support of Roswell investigators. The FIASR is recognized by the International Society for the Advancement of Cytometry (ISAC) as one of only 14 world-wide Shared Resource Laboratories for operational excellence and adherence to best practices. The Cancer Center has made a strategic commitment to the expansion of immune- and cell-based therapies consequently increasing the demand for laboratory support for translational biomarkers and clinically-based patient monitoring. FIASR provides an exceptional and essential resource for exploring the biology underlying these new therapeutic modalities. The shared resource improves fiscal and operational efficiencies and the rigor and reproducibility of assays due to the application of ISAC approved standardized maintenance, operating and validation protocols ultimately facilitating implementation of these techniques in the clinical realm. In addition to serving Roswell Park and local research institutions, FIASR serves as a core facility for several biopharma and NIH multi-site clinical trials.
Equipment technologies and services
In addition to the data acquisition software for the equipment listed in the Table, the following analysis software packages are available, free of charge to users: WinList and ModFit (Verity), FCSExpress (DeNovo), IDEAS (Amnis); AMNIS-AI; FlowJo (BD Bioscience), OMIQ, VisioPharm and ImagePro (MediaCybernetics). An internal network on a server managed by the Cancer Center’s IT department with expandable storage capacity has been set up for the data management. All investigators within the facility have password-protected access to this network from their desktop PC’s.
Other support equipment include: Cold room, fume hoods, autoclave and glass washing facilities, 3 CO2 incubators, 3 Bioguard laminar flow tissue culture hoods, benchtop centrifuges, refrigerated microfuges, inverted and conventional microscopes with phase contrast, fluorescence capacity and digital camera attachments, PCR, -80 freezers and liquid N2 storage tanks, ELISA reader, and smaller equipment necessary for cellular and molecular studies.
Major Services of the FIASR: (i) Conventional, full spectrum and mass flow cytometry, (ii) Sorting, (iii) Imaging flow cytometry, (iv) Spatial multi-omic analysis, (v) Live cell imaging, (vi) Luminex multiplex bead assays, (vii) Single Cell Secretome analysis, (viii) Nanoparticle sizing, (ix) ELISPOT, (x) ELISA, (xi) Education and training on all of the above, (xii) Sample preparation and analysis for all of the above.